Pollution

Odds are, you’ve heard the word pollution in a variety of contexts — that’s because there are numerous different kinds of pollution. So before getting into the main types of pollution that harm our environment, it's important to understand exactly what pollution means.
What does pollution mean?
Essentially, pollution is when an environment is contaminated with something whose presence negatively affects the natural order of the environment. Pollution typically refers to aspects of nature, ranging from the ocean to the soil to the atmosphere.
What is ocean pollution?
Ocean pollution is when something that does not belong in the ocean enters the ocean — and that's mostly plastic and other trash. Ocean plastic negatively affects marine life and ecosystems — meaning it also negatively affects humans.
Facts about ocean pollution:
Oceans cover more than 70 percent of the Earth, according to the NRDC — so it’s safe to say that it’s in humans’ best interest to protect them. But according to Our World, there are 5.25 trillion pieces of plastic debris in the ocean, which is pretty wild, considering plastic was only invented in 1907. That’s not exactly a good example of humans protecting the ocean, is it?
Where does ocean plastic come from?
Ocean plastic comes from humans. The greatest source of ocean plastic is from fishing nets, which account for about 46 percent of ocean plastic, at least in the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, according to a study published in Scientific Reports and as reported by National Geographic. Where does the rest of the ocean's plastic come from? In the study, most of the other ocean plastic found was additional items from the fishing industry, such as ropes, eel traps, and crates, the study added.
The commercial fishing industry employs a process called trawling, which is when a large fishing net is pulled through the ocean, gathering fish as well as accidental “bycatch,” such as dolphins, porpoises, sea turtles, and more. Unfortunately, many fishermen leave their nets and other gear behind in the ocean, causing animals to get tangled in them and die.
The remainder of ocean plastic comes from items human use, such as straws, food packaging, grocery bags, and drink bottles, as well as microplastics that shed from clothing and from plastic items trying to break down. Unfortunately, many sea animals mistake these items for food, and ingesting them can cause death. Additionally, when humans eat fish or shellfish, they are in turn ingesting the microplastics that were in the animal’s body.
How can I fight ocean pollution?
The best way to reduce your contribution to ocean pollution is by not eating sea animals. You can also use as little single-use plastic as possible, and make steps toward a zero-waste or low-impact lifestyle. Additionally, you can pick up trash whenever possible, especially on beaches, to prevent litter from entering the oceans.
What are crude oil spills?
Crude oil is unrefined petroleum product and a fossil fuel. It is used for things like gasoline, jet fuel, heating, paraffin wax, tar, and more.
Oil spills are usually accidents, occurring when oil platforms, refineries, tankers, or ships spill crude oil into the ocean, according to a study published by Science Direct. As explained by the NOAA, things like equipment malfunctioning, human error, or natural disasters are often the cause of these accidental spills. But sometimes, cruise ships will purposely dump oil-contaminated waste into the ocean, which can get the cruise companies into serious legal trouble.
When crude oil pollutes the ocean, it in turn pollutes the ocean’s inhabitants. As noted by the NOAA, oil can damage marine mammals’ coats, ruining their insulation or water-repelling capabilities; crude oil is also poisonous, and if a sea animal swallows it, it can be deadly.
How can oil spills be cleaned?
According to the NOAA, there a variety of ways to clean up oil spills, including: “sorbent” sponges that absorb oil; “in situ burning,” which burns recently-spilled oil that is floating on the water’s surface; chemicals that break oil down into its chemical components; vacuum trucks; and more.
What is air pollution or atmospheric pollution?
Air pollution or atmospheric pollution is when a harmful gas, material, chemical, or particle enters the air. According to National Geographic, some of the most prominent air pollutants are greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane, which are caused by a variety of activities, and which both contribute to the greenhouse effect, and therefore to climate change. Other common atmospheric pollutants include, soot, mold, pollen, asbestos, cigarette smoke, and ozone, National Geographic added.
Why is air pollution harmful?
As mentioned earlier, greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are a form of pollution because they contribute to climate change. As for the other atmospheric pollutants, many of them can have negative impacts on human health. According to the World Health Organization and National Geographic, ambient air pollution can cause illnesses like strokes, lung cancer, respiratory infections, and heart disease, and in 2016, air pollution was responsible for an estimated 4.2 million deaths globally.
How can I reduce air pollution?
To contribute to less atmospheric pollution, you can: take measures to conserve energy, such as using energy-efficient light bulbs, appliances, and more; rely on public transportation, walking, or biking instead of driving a car; send less trash to landfills, where garbage emits harmful greenhouse gases; eat less animal products, since livestock emits significant amounts of methane; and use eco-friendly household products such as paints and cleaning products.
What is land pollution?
Land pollution is when land or soil is contaminated by a variety of environmental pollutants. According to the Conservation Institute, the major causes of land pollution are: industrialization, deforestation (which can cause soil erosion), landfills (which pollute the soil and the air), mining, sewage, and agriculture (both the chemicals used on crops and the runoff from animal agriculture).
Why is land pollution harmful?
Land pollution can lead to a number of harmful consequences on the environment. According to Conserve Energy Future and the Conservation Institute, land pollution can cause: soil erosion; climate change; various negative effects on human health; air pollution; the destruction of animal habitats; a higher risk of wildfires; and more.
How can I reduce land pollution?
To reduce your contribution to land pollution, you can: reduce your consumption of single-use plastic and try to send less rubbish to landfills; make sure to responsibly dispose of toxic chemicals, such as cleaning products, aerosol cans, and paint; eat less animal products such as meat, dairy, and eggs, since livestock is responsible for significant land pollution and air pollution; eat or grow organic produce when possible (check out the Dozen and Clean 15 for more information); plant trees; and donate to organizations that plant trees.
Latest Pollution News and Updates

These Carpet Cleaning Appliances Can Also Improve Indoor Air Quality
These carpet cleaners tackle dust, dirt, mold spores, dander, and more pollutants and allergens hiding in your rugs before they get back into the air.
How to Choose the Best Air Purifier for Mold — Our Top 5 Energy Star-Approved Picks
These energy-efficient air purifiers all have HEPA filters strong enough to get rid of mold and more than 99 percent of airborne toxins in your home.
A Georgia City Has Spilled Millions of Gallons of Raw Sewage Into 2 Pristine Rivers
For more than a decade, raw sewage spills regularly plague the Withlacoochee and Suwannee Rivers, and minimal efforts have been made to stop it.
7 Eco-Friendly Disposable Plates Made of Clever Materials Like Cornstarch and Sugarcane
These plant-based disposable plates give you the convenience of single-use dinnerware without the environmental impact and landfill waste..
Is Cheap Synthetic Fashion Killing Us? The Truth About Polyester Fabric
Do you like eating microplastics? We bet you don't! Well, your adored polyester hoodie is likely contributing to the global plastic pollution crisis.
Green Hydrogen: What It Is, How It Stacks up Against Blue Hydrogen, and More
What is green hydrogen? It may be a trendy new sustainable fuel, but how does it match up against blue hydrogen? Here's what to know.
The Plastic Making Process Is Harmful to the Environment — Here's Why
How is plastic made? The process of creating the products might be more harmful than the products themselves.
“Forever Chemicals” Are in Some Sparkling Water Brands — Here’s Which to Avoid
A study found that some popular sparkling water brands contain concerning levels of forever chemicals. You may be surprised by the results.
Air Pollution In the Bay Area Is Still a Major Concern
Air pollution in the Bay Area isn't as bad as it was a decade ago, but still poses a large threat to public health.
New York's Hudson River Has a Long History of Pollution
Hudson River pollution came about over 30 years — here's how the cleanup efforts have been going since the 1980s.
The West Virginia Chemical Spill Defaced the Elk River — and Actually Prompted Law Changes
After the West Virginia chemical spill of 2014, U.S. lawmakers changed laws regulating toxic chemicals. Prior to the spill, the chemical MCHM was unregulated.
Is All Eco-Friendly Glitter Just Greenwashing? Here Are the Best Options
We're looking into the eco glitter gel options out there.
Why This River is Considered One of the Most Contaminated U.S. Waterways
The most polluted rivers in the U.S. are threatened by toxic contaminates from industrial waste, agricultural runoff, forever chemicals, and more.
Is the U.S. Banning Gas Stoves? New York Set to Ban Them in 2026
Is a nationwide ban on natural gas stoves in the cards?
What Is a Climate Disadvantaged Community? Many NYC Neighborhoods to Receive Climate Funds
What does it mean to be climate disadvantaged? Several NYC neighborhoods have been identified as such, and will receive climate funds.
TikTok Creators Give a Look Into "Nurdles," Plastic Pollutants Straight From the Oil Industry
Known as nurdles, these plastic pellets are a frustrating form of plastic pollution that has been found in pretty much every facet of nature.
How Kotzebue, Alaska Became Known as the Country's "Most Toxic Town"
Kotzebue, Alaska is located 90 miles from the Red Dog Mine, the largest chemical polluter in the United States.
What Is Bio-Based Glue? Behind IKEA's Hottest New Material
IKEA announced its decision to transition to bio-based glue, as traditional glue contributes to about 5 percent of the company's climate impact.
What Are CFCs and Why Are They Banned? Here’s What You Need to Know
What are CFCs? Learn more about these chemicals, how they affect the environment, and why they are banned.
What Is Being Done for East Palestine, Ohio? Behind Recovery Efforts
Did FEMA deny aid to East Palestine, Ohio? After a train derailed in the small Ohio suburb, various dangerous chemicals were released into the air.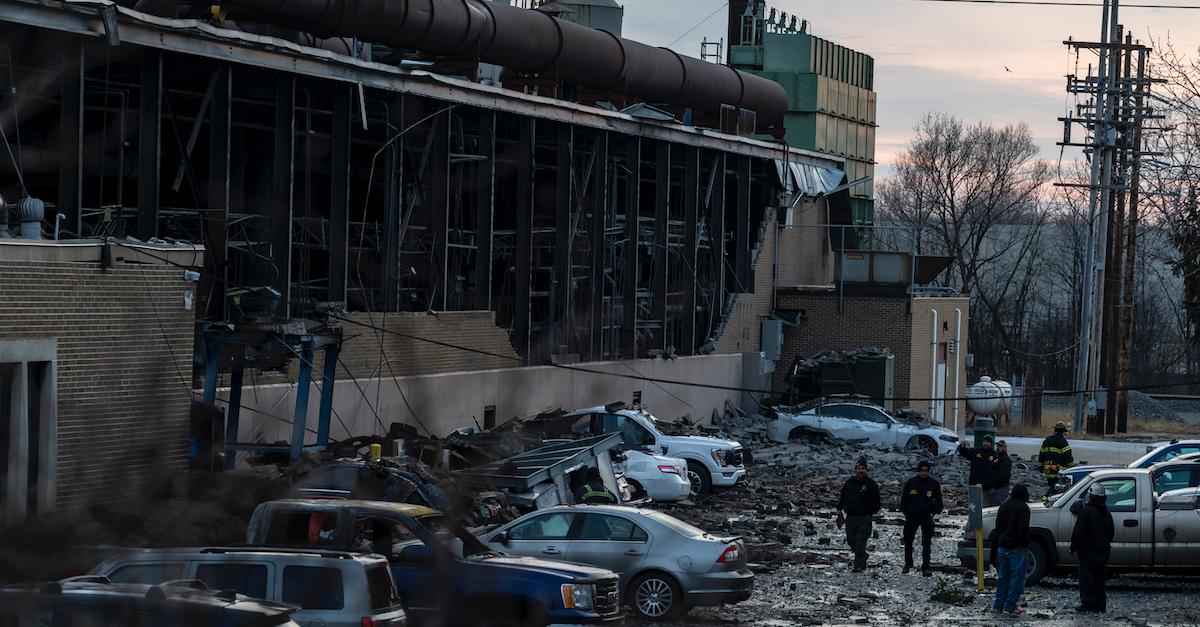
What Caused the Factory Explosion in Bedford, Ohio? What to Know About the Deadly Accident
What caused the factory explosion in Bedford, Ohio? One is dead and several are injured after a metal plant exploded with debris.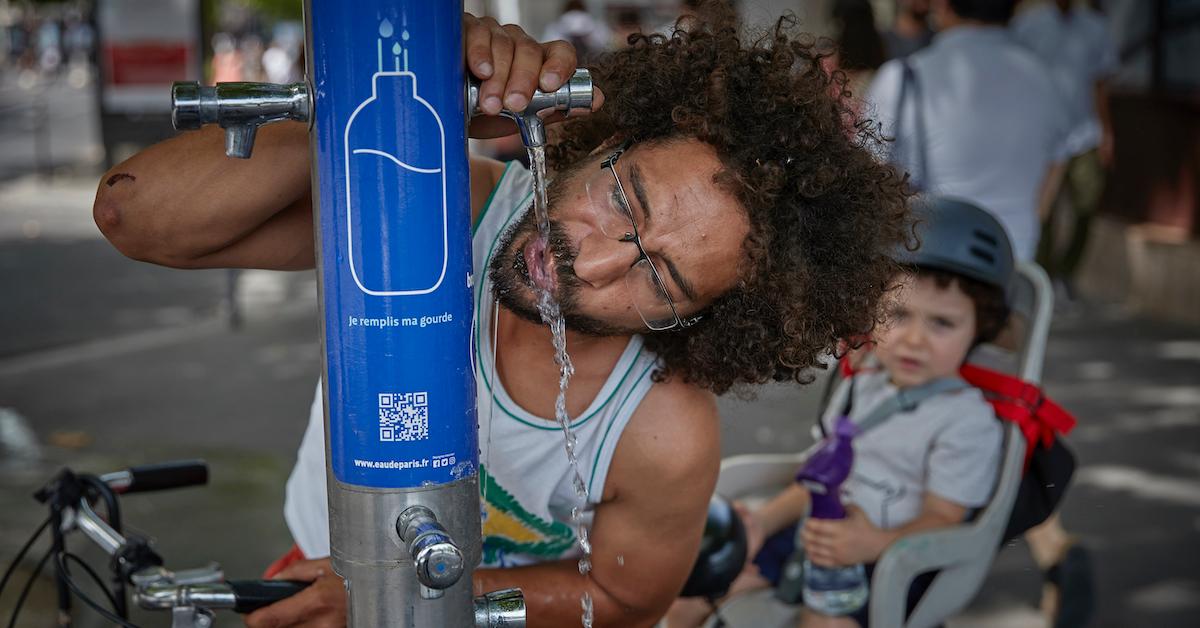
Paris’ Water System Is Elite — Here’s Why
Although water is essential to life, the city of Paris' water system is so much better than ours.
How Does Polyester Impact the Environment? Is It Eco-Friendly?
Polyester is a man-made fabric with a dubious reputation for many reasons, but just because it isn’t comfortable, does that mean it also isn’t eco-friendly?
Here’s Why Lake Michigan Is Supposedly the Deadliest of the Great Lakes
Compared to the other Great Lakes, Lake Michigan is considered to be the deadliest of them all. Here's why.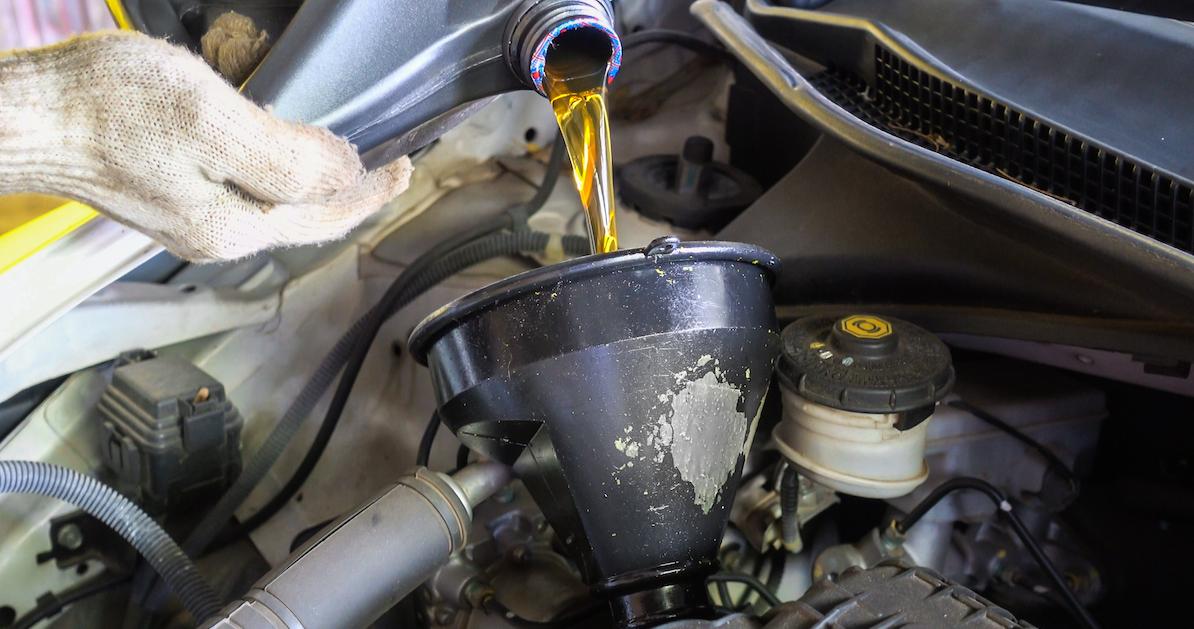
How to Recycle Used Motor Oil Instead of Trashing It
Getting rid of used motor oil can be a bit complicated, but did you know that you can actually recycle it rather than throw it away?
Freshwater Fish Nationwide Test for High Levels of PFAS, or "Forever Chemicals"
If you're a fan of freshwater fish, you may want to change your mind — species tested in the U.S. showed dangerously high levels of PFAS.
U.K. Plastic Plate Ban Is Yet Another Step Towards a Plastic-Free Nation
After announcing a potential ban on single-use plastic cutlery in 2022, the U.K. is now enforcing a highly necessary ban on plastic plates.
‘Ocean Emergency: Currents of Hope’ Documentary: What It’s About, How to Watch, and More
What is ‘Ocean Emergency: Currents of Hope’ about? The new documentary, which aired on the CW earlier this week, has garnered quite a bit of buzz.
Kettleman City, Calif. Could Have a Pesticide Problem — Here's Why
Kettleman City, Calif. has had problems concerning the rates of children born with birth defects for years. Here's why pesticides could be the reason.
Why We Must Hold Factory Farming Accountable for Deforestation and Pollution, According to New Research
The factory farming industry has an immense impact on the environment. And now, a new report shows why this ecologically-destructive industry’s environmental footprint has failed to improve.
What Is the Montreal Protocol? It’s Important to Reduce Pollution
What is the Montreal Protocol? The international treaty, which was established in 1987, aimed to regulate the production of chemicals that cause global warming.
Awful Air Quality Prompts Delhi to Enact "Pollution Ban" on Construction, Diesel Cars, and More
Delhi's air pollution news has been rough lately, with air quality levels in the area leading to a “pollution ban” in Delhi.
A Shuttered St. Croix Oil Refinery Is Currently at Risk of Exploding
A St. Croix oil refinery, called Limetree Bay, closed in 2021. But chemical releases continued sickening locals, and it's now at risk of explosion.
How to Remove “Forever Chemicals” Using Reverse Osmosis
Figuring out how to remove PFAS from water can seem complicated. But there are a few methods, such as reverse osmosis, that you can try.
Tesla Is in Hot Water After Underreporting Environmental Data
What is Tesla's 2022 controversy about? Environmentalists are furious with the sustainable car company 2022 for underreporting environmental data.
Filming Disney+’s ‘America The Beautiful’ Was Bittersweet (Exclusive)
Although filming 'America the Beautiful' was a fulfilling journey, cinematographer Greg Wilson tells us what it was like filming the effects of climate change.
The EPA Has Lowered the “Healthy” Levels of Forever Chemicals in Drinking Water
Although PFAS, or forever chemicals, are incredibly ubiquitous, the EPA says the "healthy limit" of consuming them is lower than previously thought.
Here’s How Noise Pollution Affects the Environment
Although noise pollution doesn't involve actual pollutants, its environmental impact is shockingly high.
Cooking Is More Pollutive Than We Thought — Here’s Why
What is the environmental impact of cooking? Depending on how you're cooking your food, you may be releasing aerosols into the atmosphere.
Perchlorate, Which Has Been Linked to Infant Brain Damage, Still Unregulated By EPA
Why isn't the EPA regulating perchlorate levels in drinking water? The chemical has been linked to a wide variety of health problems nationwide.
This Heavily Polluted Waterway May Finally Get a Much-Needed Cleanup
On Thursday, March 31, the EPA is going to outline plans to clean up the Lower Duwamish Waterway in Seattle, Wa.
Half of U.S. Waterways Too Dirty to Swim, Fish, or Drink From, Report Finds
A report by the Environmental Integrity Project estimates that about 50 percent of waterways in the U.S. are too dirty to fish, swim, or drink.
London Alerts City Dwellers of Toxic Air Quality With High Pollution Warning
The London government has issued an air pollution warning for city dwellers to be aware of the “extremely dangerous” high air pollution index.
Biden to Reduce Heavy Truck Pollution With Newly Proposed Rule
What is Joe Biden doing to address pollution? The POTUS is tackling air pollution by proposing a new rule that would cut heavy truck pollution.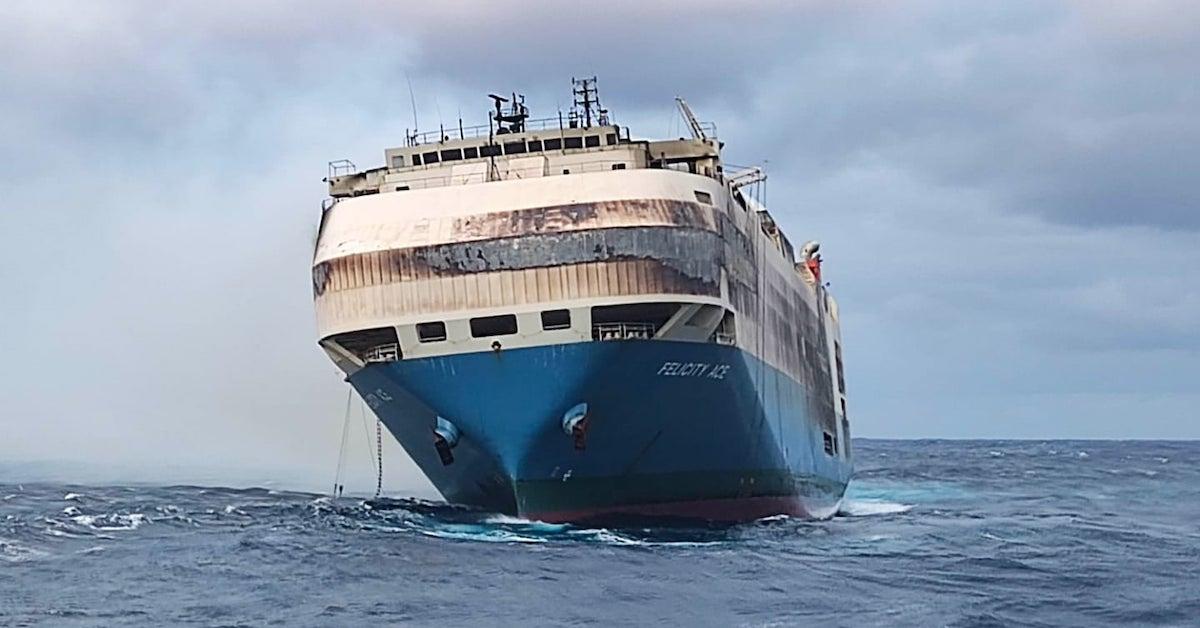
Volkswagen Ship Carrying 4,000 Luxury Cars Sinks, Could Potentially Leak Oil Into Atlantic Ocean
The Felicity Ace cargo ship, which was transporting luxury cars, just sank, sending the entire ship, 4,000 brand new cars, and thousands of tons of fuel and oil to the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean.
Marine Life Still Feeling the Effects of the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill, Years Later
Although the Deepwater Horizon oil spill happened years ago, dolphins are still feeling the effects — and will continue to, with new drilling plans.
Biden Invests $1 Billion in a Major Great Lakes Cleanup
After enduring years of pollution, a Great Lakes cleanup is finally taking place — but what will that entail, and why are the Great Lakes so polluted?
Drugs Are Polluting Our Rivers — Threatening Humanity and the Environment
What is drug pollution? Unfortunately, pollution from pharmaceutical waste is overflowing into our rivers, posing a risk to humans and nature.
Chemical Pollution Levels Have Surpassed a Safe Limit for Life on Earth, Study Shows
Scientists have conducted a study that shows Earth's chemical pollution has passed the safety limit, from an environmental and public health stance.
What Is 1-Bromopropane, and Why Is It So Dangerous?
What is 1-bromopropane? For the first time in three decades, the chemical, which is found in dry cleaning, stain removers, adhesives and cleaners